Zinc-nickel plating is widely used across industries where metal parts face extreme environments, including automotive, wind energy, oil & gas, and infrastructure. But what coating thickness is ideal? And how many salt spray hours define a reliable zinc-nickel finish?
Zinc-nickel coatings are usually applied at 5–10µm thickness. For parts without passivation, 10µm zinc-nickel must withstand at least 500 hours of neutral salt spray test (ASTM B117 or ISO 9227) without red rust. Some advanced coatings like Zn-Ni-Tin can reach over 1400 hours. In comparison, regular zinc coating only holds about 120 hours before corrosion appears.
Zinc-nickel coating not only helps extend the service life, but also reduces maintenance and replacement cost in the long run. Below we share with you some key standards, test methods, and reasons why zinc-nickel is often chosen for critical applications.

What is the ASTM standard for salt spray test?
The most widely accepted salt spray test is defined in ASTM B117. This neutral salt spray (NSS) test exposes coated metal samples to a continuous fog of 5% NaCl solution, and pH range is controlled at 6.5–7.2.
Zinc-nickel parts are usually tested from 500 to 1000 hours, depending on coating thickness and post-treatment. But for zinc-only coating, it always fails much earlier—only 120–200 hours under the same test conditions.
What is the ASTM standard for zinc nickel plating?
Zinc-nickel coating is produced per ASTM B841 standard, which clearly defines its composition, thickness range, and inspection requirements. If it’s zinc-only coating, then ASTM B633 should be used instead.
Many customers from automotive, energy, and aerospace industries choose ASTM B841 when long-term durability is a must. This standard allows 12–16% nickel content, which is proved to offer strong anti-rust performance.
How to check zinc-nickel plating thickness?
The most accurate method is X-ray fluorescence (XRF). This non-destructive test measures coating thickness down to microns, ideal for fasteners, connectors, and complex geometries.
There are also other methods:
- Microscopy (cross-sectioning) – very accurate, but it’s a destructive method
- Magnetic methods – fast, but less accurate for very thin coatings
- Eddy current testing – suitable for non-ferrous substrates
What is the ISO standard for salt spray test?
ISO 9227 is the international counterpart to ASTM B117. It includes:
- NSS (Neutral Salt Spray) – standard for zinc-nickel evaluation
- AASS (Acetic Acid Salt Spray) – for decorative coatings
- CASS (Copper Accelerated Salt Spray) – for severe conditions
For zinc-nickel, ISO 9227 NSS is the primary method, requiring no red corrosion before 500–720 hours, depending on the application.
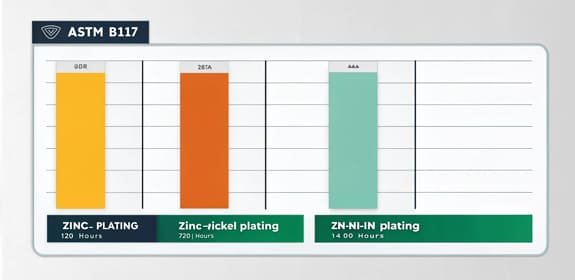
How many hours can zinc-nickel coating withstand in salt spray tests?
Typical zinc-nickel coatings with 10µm thickness can resist:
- ≥ 500 hours without red corrosion (standard pass level)
- ≥ 720 hours with topcoat or passivation
- Up to 1400 hours for Zn-Ni-Tin formulations in advanced applications
By comparison, zinc-only coatings fail at ~120–200 hours in NSS, making zinc-nickel significantly more robust.
What is the difference between zinc plating and zinc-nickel plating?
| Feature | Zinc Plating | Zinc-Nickel Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Thickness | 5–8 µm | 5–10 µm |
| Salt Spray Resistance | ~120 hrs | ≥500–1400 hrs |
| Cost | Lower | Moderate |
| Corrosion Protection | Basic | High |
| Industries | General | Automotive, Offshore, Industrial |
Zinc-nickel offers sacrificial protection like zinc but with superior resistance due to nickel’s barrier effect.
Why do automotive and industrial buyers prefer zinc-nickel coatings?
For automotive buyers, zinc-nickel is often Tier 1 and Tier 2 standard due to:
- >1000 hours corrosion protection
- Compatibility with ISO/DIN specs
- Cost-effective vs. stainless steel
Wind energy, power transmission, and municipal infrastructure projects value zinc-nickel for:
- Outdoor reliability
- Long-term resistance to rain, fog, and chemicals
- Compliance with OEM and government specs
How do zinc-nickel coating requirements vary by application?
| Industry | Minimum Thickness | Salt Spray Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | 8–10 µm | ≥720 hrs (ASTM B117) |
| Oil & Gas | 10 µm | ≥1000 hrs |
| Wind Energy | 10 µm + topcoat | ≥1200 hrs |
| Industrial Fasteners | 5–8 µm | ≥500 hrs |
| Municipal Projects | 8 µm | ≥720 hrs |
Coating systems may include trivalent chromates, sealants, or organic topcoats depending on specifications.
How thick should zinc-nickel coating be for optimal performance?
- 5 µm – Suitable for indoor or low-corrosion settings
- 8 µm – Balanced protection for light-duty outdoor use
- 10 µm – Industry standard for automotive, offshore, infrastructure
- >10 µm – Required in extreme applications (e.g., offshore rigs, wind turbines)
For most buyers, 10 µm is the sweet spot balancing protection and cost.
Can zinc-nickel coating replace stainless steel in coastal applications?
In many cases, yes. Zinc-nickel offers similar corrosion resistance when properly applied and tested, at a fraction of the cost. While stainless steel remains unmatched in some structural applications, zinc-nickel is a practical substitute for:
Its sacrificial protection ensures the base metal stays intact even if the coating is scratched.

Conclusion
Zinc-nickel coating can offer strong rust protection even with only 5–10 µm thickness. When tested by ASTM B117 or ISO 9227 salt spray, it lasts hundreds of hours longer than regular zinc plating. Whether you’re buying for automotive, offshore, or municipal applications, understanding these coating and test standards ensures better product longevity and fewer failures.
Contact Hengrui Fastener for Custom Zinc-nickel bolt
For specialized applications that require custom solutions, Hengrui Fastener offers high-quality, customizable Zinc-nickel bolt and fasteners. Whether you need a specific size, material, or finish, Hengrui can provide tailored fasteners to meet your exact requirements. Contact Hengrui Fastener to learn more about our products and services.






