What is a Spring Washer?
Spring washers, also called disc springs or Belleville washers, have a unique conical shape that compresses and flattens when a load is applied, providing spring force. This is essential to prevent loosening caused by vibration.
Another variation is the wave spring washer, which has a wavy, undulating shape that provides less spring force over a larger range of motion.
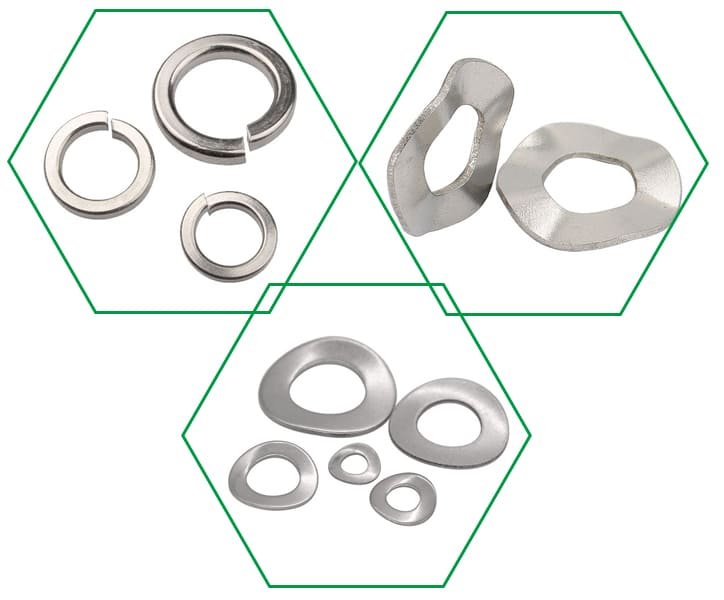

Usually made from high carbon steel, stainless steel, or elastic materials, they can withstand significant deformation without losing shape or elasticity. This makes them not too much in terms of material selection, but highly specialized in terms of dynamic loading.
Common sizes for spring washer include M3, M4, M5, M6, M8, M10, M12, 1/4″, 5/16″, and 1/2″, catering to a wide range of bolt diameters.
What is the advantage of Spring Washers?
- Load Distribution: Helps distribute the load evenly, especially beneficial in cases where the joint faces are soft or irregular.
- Absorb Shock: They effectively absorb shock, helping to protect the integrity of the assembly by reducing the load and stress transitions between the bolt and the nut.
- Preventing Loosening: They prevent loosening of the fastening assembly caused by vibrational forces by exerting a continuous load, thus ensuring that the assembly remains tight and secure.
- Compensating Spring Force: The inherent design of spring washers applies a constant force to the bolt head or nut and underlying surface, thus counteracting the bolt’s tendency to loosen.
What is a Flat Washer?
Flat washers also called Plain washers, It has a flat, thin plate, usually round, with a hole in the center. The outer diameter of a washer is significantly larger than the inner diameter, allowing it to distribute the load of a fastener, such as a screw or bolt, over a wider area, reducing wear and preventing damage to the material being fastened.

Flat washers are available in a wide variety of materials, including but not limited to metal, plastic, copper, and rubber, making them versatile and suitable for a variety of applications, environments
The choice of material depends on the application’s specific needs, such as required strength, corrosion resistance, or electrical conductivity. They are also available in many sizes to meet a variety of bolt sizes and load requirements.
Common sizes for flat washers include M4, M5, M6, M8, M10, M12, 1/4″, 5/16″, 3/8″, and 1/2″, catering to a wide range of bolt diameters.
What is the advantage of Flat Washer?
- Load Distribution: By providing a larger surface area, they spread the load over a wider area than just the bolt head or nut, which helps reduce pressure on the material being secured.
- Preventing Surface Damage: They protect the surface of the assembled parts from damage during the tightening process. This is crucial for softer materials that might otherwise be marred or indented by the fasteners.
- Spacer and Shim: Flat washers can act as spacers or shims, providing precise adjustments in mechanical applications to ensure proper clearance and alignment.
- Reducing Friction: During the tightening process, washers help reduce friction between the bolt or nut and the material, facilitating smoother installation and preventing the fastener from seizing or binding.
Common sizes for flat washers include M4, M5, M6, M8, M10, M12, 1/4″, 5/16″, 3/8″, and 1/2″.
What is the difference between spring washer and flat washer?
When selecting washers for any application, understanding the differences between spring washers and flat washers is essential to ensure joint stability and longevity. Here are the main differences between these two types of washers:
Shape and Design Differences:
- Spring Washers: Spring Washers: They are characterized by a unique conical or curved shape. This design enables the washer to act as a spring, allows the washer to exert a load or tension against a bolt and the assembly, enhancing the fastening’s resistance to loosening under vibrations or thermal expansion.
- Flat Washers: These are simple, flat discs with a hole in the center. They are designed to as a buffer or protective layer between the bolt or nut and the surface of the assembled parts.
Functional Differences:
- Load Distribution:
- Spring Washer: Not primarily designed for load distribution; its main function is to maintain preload and tension in a bolted connections.
- Flat Washer: Helps distribute the load of a bolt or screw over a larger area than the fastener alone would, which can prevent damage to the surface of assembled parts and distribute the clamping force more evenly.
- Resistance to Loosening:
- Spring Washer: Ideal for preventing fasteners from loosening due to vibration or temperature changes, because of its spring action keeps constant tension on the fastener.
- Flat Washer: By itself it does not prevent loosening under vibration, unless used in combination with other locking mechanisms such as locking nuts or thread locking fluid.
Applications Differences:
- Spring Washer Uses:
- Suitable for use in applications where joint integrity is crucial under conditions of high vibration, dynamic loads, or thermal cycling conditions. Commonly found in automotive, manufacturing, and engineering applications where bolts are subject to regular movement or stresses that might cause loosening.
- Flat Washer Uses:
- Suitable for applications where the primary concern is surface protection or load distribution, such as in construction, furniture assembly, and general manufacturing. Flat washers are used to protect surfaces from damage during the tightening of fasteners and to prevent pull-through or tearing.
Effectiveness Over Time
- Spring Washers: Can maintain bolt tension effectively over time under the right conditions, but may lose their elasticity if over-compressed or overloaded.
- Flat Washers: Remain effective as long as they are not worn down or corroded, because they do not rely on mechanical properties beyond their thickness and material strength.
What is the installation sequence of spring washer or flat washer?
When using both a flat washer and a spring washer together, the flat washer is usually used first, placed directly under the bolt head or nut, followed by the spring washer.

Because the flat washer provides a smooth, even surface that helps distribute the load more evenly, which protects the surface of the component. Placing the flat washer first also allows the spring washer to apply spring force directly against the flat washer, enhancing the spring washer’s effectiveness at maintaining tension and preventing the bolt from loosening due to vibrations or oad changes.
This setup takes the advantage of both types of washers — protection and load distribution of the flat washer, and tension maintenance of the spring washer — ensuring the integrity and longevity of the fastened joint.
Considerations for Choosing Between Spring Washer and Flat Washer
When choosing between a spring washer or a flat washer, consider the following factors:
- Application Environment: If the component is frequently subject to vibration, temperature fluctuations or dynamic loads, it is best to use spring washers.
- Surface Protection and Load Distribution: If the goal is to protect the surface of the material being fastened or to distribute the load more evenly, a flat washer is the preferred choice.
- Bolt Size and Load: Make sure the washer fits the bolt size and can handle the load requirements.
When should spring washers vs. flat washers be used?
When should spring washers be used: In applications where the joint may move or vibrate, such as in engines or moving machinery parts.
Consequences of Not Using Spring Washers: Failure to use spring washers in vibration-prone environments may cause bolts to loosen, resulting in joint failure or mechanical failure.

When should flat washers be used: In applications where the load needs to be evenly distributed over a larger surface area, such as in woodworking or when fastening softer materials.
Consequences of Not Using Flat Washers: Without flat washers, the pressure exerted by the fastener could cause damage to the material, leading to weakened joints and potential failure.

Understanding their functions and selecting the correct grade and material based on the application’s specific needs can significantly enhance improve component performance and safety.






