What is the Locking Nut?
The locking nut, also known as a: nut with lock, locknut, lock nut, self-locking nut, stiff nut or prevailing torque nut, is a specially designed nut that is a fastener that prevents loosening or backing out due to vibration or torque.

Unlike regular nuts, which may loosen over time, nut with lock offer added security and reliability for a more secure hold.
Compared with standard nuts, self-locking nut have the following advantages:
- Strong anti-loosening performance: Due to the existence of the locking mechanism, self-locking nut are not easy to loosen under vibration conditions
- Widely used: Can be used in various occasions that require high safety and stability, such as aerospace, railways, mechanical equipment, and other high-vibration environments
However, nut with lock also has some disadvantages:
- Higher cost: Due to the complex structural design, the manufacturing cost is usually higher than that of ordinary nuts
- Difficult to disassemble: Due to the existence of the locking mechanism, locking nuts require greater force when disassembling, and sometimes they cannot even be reused
How does a Locking Nut Work?
Locking nuts are usually divided into two different locking principles:
- One is to use the elastic deformation of the metal itself to produce locking effect, such as nylon lock nut, which embed nylon rings in the nut to increase friction and thus lock.
- The other is through the design of special threads or structures to achieve self-locking, such as all-metal locking nuts, through the threads of the self-locking performance to enhance the anti-loosening ability of the nut.
What are the types of Nut with Lock?
Here’s a detailed look at the different types of lockable nuts, their unique features, and their specific applications:
1. Nylon Insert Nut with Lock( Self locking nut )
Mechanism:
- These nuts feature a nylon collar insert that creates friction between the nut and the bolt, preventing loosening.
- The nylon insert deforms over the threads, increasing resistance to vibration and movement.
- Not recommended for multiple uses, as the nylon insert may wear out after the first use, reducing its effectiveness.

Advantages:
- Effective for reducing loosening due to vibration.
- Suitable for a wide range of applications.
Applications:
- Automotive industry
- Machinery and equipment
- General industrial use
2. Keps K-Lock Nuts
Mechanism:
- These nuts have an attached free-spinning washer that provides additional friction and locking action when tightened.
- The washer helps distribute the load and prevents loosening due to vibration.

Advantages:
- Integrated washer simplifies assembly and provides consistent locking force.
- Suitable for a wide range of applications where vibration is a concern.
- Reusable, but the attached washer may wear out over time, reducing its effectiveness.
Applications:
- Electronics
- Machinery and equipment
- Automotive applications
3. Stover Nuts with Lock
Mechanism:
- Also known as top locking nuts, Stover nuts have a conical top that creates a locking action through friction when tightened onto the bolt.
- The deformed threads create resistance against loosening.

Advantages:
- High strength and reliability.
- Suitable for high-vibration environments and heavy-duty applications.
- Typically reusable, but their effectiveness may decrease slightly with each reuse due to wear on the threads.
Applications:
- Construction equipment
- Heavy machinery
- Automotive industry
4. Serrated Flange Locking Nuts
Mechanism:
- These nuts have serrations on the flange that dig into the mating surface when tightened.
- The serrations increase the friction between the nut and the surface, preventing loosening.

Advantages:
- Effective in distributing the load over a larger area, reducing the risk of damage to the mating surface.
- Provides additional locking force without the need for a separate washer.
- Reusable, but the effectiveness of the serrations may diminish with repeated use.
Applications:
- Applications where the bolt or screw is installed against a flat surface
- Structural assemblies
5. Locking Wheel Nuts (Locking Lug Nuts)
Mechanism:
- These nuts are designed specifically for securing wheels on vehicles.
- Often feature a unique pattern that requires a special key to remove, preventing theft.

Advantages:
- High security for vehicle wheels.
- Prevents unauthorized wheel removal.
- Generally reusable, but the locking mechanism’s effectiveness should be checked periodically.
Applications:
- Automotive industry
6. Jam Nuts (also called half lock nut)
Mechanism:
- These are thin nuts used in conjunction with a standard nut to lock the assembly in place.
- The jam nut is tightened against the standard nut, creating a locking action.
Advantages:
- Simple and cost-effective locking solution.
- Easy to install and remove.
- Reusable, with minimal wear over multiple uses.
Applications:
- General mechanical applications
- Light-duty applications
7. Castellated Nuts (Castle nut) and Slotted Nuts
Mechanism:
- Castellated Nuts: These nuts have slots (or castellations) cut into one end. A cotter pin is inserted through a hole in the bolt and the slots in the nut to prevent rotation.
- Slotted Nuts: Similar to castellated nuts, but with fewer and larger slots. They also use a cotter pin for locking.
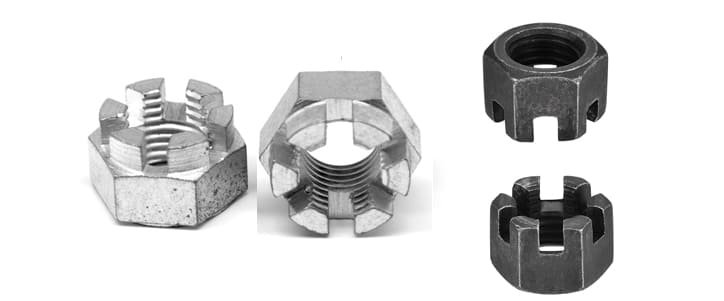
Advantages:
- Extremely secure locking mechanism that prevents the nut from loosening, even under severe vibrations and loads.
- Suitable for applications where regular inspection and maintenance are possible.
- Reusable, provided the cotter pin or other locking device is replaced each time the nut is reused.
Applications:
- Automotive and machinery where safety is crucial.
- Heavy equipment and machinery assemblies.
- Applications where a high degree of security against loosening is required.
What are the Benefits of Using Locking Nuts?
- Vibration Resistance: Locking nuts are specifically designed to resist the effects of vibration and dynamic loads, ensuring a secure assembly over time.
- Improved Safety: By preventing accidental loosening, nut locking contribute to the safety and reliability of mechanical systems.
- Durability: High-quality locking nuts can withstand harsh environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures and exposure to chemicals.
- Reusability: While some lock nuts, such as nylon insert lock nuts, may degrade with repeated use, many types of lock nuts, can be reused multiple times without losing their effectiveness.
How to Choose the Right Locking Nut?
When selecting a locking nut for your application, consider the following factors:
- Application Environment: Determine if the nut will be exposed to high temperatures, chemicals, or extreme vibrations.
- Load Requirements: Ensure the nut can handle the mechanical loads and stresses of your application.
- Material Compatibility: Choose a locking nut material that is compatible with the bolts or screws and the overall assembly.
- Reusability Needs: Decide if the nut needs to be reused multiple times or if a single-use solution is acceptable.
FAQs:
Q1: What materials are locking nuts made from? A: Locking nuts are typically made from stainless steel, carbon steel, or alloy steel. Some may have coatings for additional corrosion resistance.
Q2: Are custom locking nuts available? A: Yes, custom locking nuts can be manufactured to meet specific design and performance requirements. Companies like Hengrui as fastener manufacturer, specialize in producing custom fasteners.






