Choosing the right coating for industrial fasteners is very important. It may affect the performance and service life of your products. In harsh working environments, rust and wear are serious issues. Below is a brief comparison of Zinc and Zinc-Nickel plating. Hope this can help you or your engineering team select the most suitable option based on actual usage and budget.
Zinc-Nickel plating offers superior corrosion resistance, temperature tolerance, and wear protection compared to standard Zinc plating, making it ideal for demanding environments such as marine, automotive, and energy sectors. Zinc plating, while cost-effective and widely used, is better suited for general-purpose applications with moderate corrosion exposure.
Let’s take a look at key factors—corrosion, durability, environmental aspect, and cost—for your evaluation.
What Makes Zinc-Nickel Plating More Corrosion-Resistant?
In industrial settings, corrosion resistance directly impacts fastener life and system integrity. Zinc-Nickel plating outperforms standard Zinc plating by a wide margin.
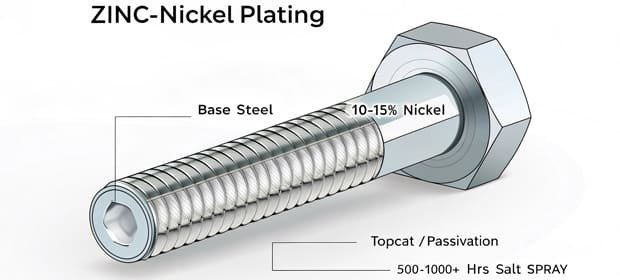
Zinc plating typically withstands about 120 hours of neutral salt spray before red rust appears. In contrast, Zinc-Nickel coatings can resist over 500 hours, and even reach 1000+ hours when combined with topcoats and passivates.
This makes Zinc-Nickel a superior option for:
- Marine and coastal applications
- High-humidity or industrial gas environments
- Aerospace, defense, and electrical towers
Which Coating Handles High Temperatures Better?
Temperature fluctuations can degrade coatings over time. Here’s how these two options compare:
Zinc-Nickel can resist high temperature up to 120°C (248°F) and maintain its performance. Very suitable for high-heat areas like under-hood parts in cars, or wind turbine components.
Zinc plating has moderate thermal tolerance, effective up to 49°C (120°F) and sometimes holding up to 204°C (400°F) depending on the substrate and post-treatment.
If your fasteners work in hot zones, Zinc-Nickel would be safer in the long run.
Durability & Mechanical Performance: Which Lasts Longer?
In high-wear applications like bolted joints under vibration or repeated disassembly, Zinc-Nickel wins for mechanical durability:
- Hardness & wear resistance: Zinc-Nickel is significantly harder than Zinc, providing better wear protection during installation and service.
- Adhesion & uniformity: Zinc-Nickel forms more even coatings, allowing flexibility for cold-forged or bent components.
- Zinc plating is more ductile but can wear off faster under stress or frequent torqueing.
For automotive and heavy machinery OEMs, this makes Zinc-Nickel more compatible with performance-driven requirements.
How Do the Coatings Affect Environmental Compliance?
Both options are environmentally friendly, but Zinc-Nickel has advantages when replacing hazardous cadmium:
- Zinc-Nickel plating is widely seen as a cadmium-free alternative that complies with REACH and RoHS standards, especially useful in EU and Japan markets.
- Zinc plating is recyclable, cost-effective, and widely available. It remains the go-to solution for general-purpose, low-to-medium risk applications.
If your customers have higher requirements on environmental standards, Zinc-Nickel is a better option.
Which Is More Cost-Effective and Easier to Apply?
Zinc plating is cheaper and fast to process—ideal for high-volume orders without high durability requirements.
Zinc-Nickel is more costly due to tighter nickel control (10–15%) and complex process. But in harsh conditions, it reduces replacement frequency and maintenance cost, which means lower cost in the long term.
Distributors for automotive, energy or infrastructure clients often stock both.
When Should You Use Zinc Plating vs Zinc-Nickel Plating?
| Scenario | Best Coating |
|---|---|
| General machinery bolts | Zinc |
| Construction or MRO use | Zinc |
| Marine or coastal infrastructure | Zinc-Nickel |
| EV battery frames or connectors | Zinc-Nickel |
| Aerospace or wind tower systems | Zinc-Nickel |
For critical systems, longevity and performance outweigh upfront savings. Zinc-Nickel is the smarter investment.
Zinc-Nickel vs Zinc Plating: Summary Table
| Attribute | Zinc Plating | Zinc-Nickel Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Good (~120 hrs salt spray) | Excellent (500–1000+ hrs salt spray) |
| Temperature Resistance | Moderate (up to 120°F to 400°F) | Higher (up to 248°F and beyond) |
| Hardness & Wear | Relatively low | Higher hardness, better wear resistance |
| Cost | Lower | Higher (specialized process) |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly | Cadmium-free, RoHS-compliant |
| Best for | Construction, automotive, machinery | Marine, defense, EV, aerospace, energy sectors |
FAQ: Common Questions About Zinc and Zinc-Nickel Plating
What is the difference between zinc and zinc-nickel plating?
Zinc-Nickel is an alloy coating with 10–15% nickel, offering enhanced corrosion resistance and hardness over pure Zinc plating. It performs better in salt spray and harsh environments.
Is zinc-nickel better than zinc?
Yes. Zinc-Nickel lasts 4x–10x longer in corrosive conditions, making it a better choice for demanding industries like automotive and marine applications.
Why use zinc-nickel plating for fasteners?
Zinc-Nickel provides a durable, uniform finish, withstands higher heat, and resists red rust for extended periods. It’s ideal for critical safety parts like suspension or chassis bolts.
How long does zinc-nickel plating last?
With proper topcoats, Zinc-Nickel can exceed 1000 hours in salt spray tests, compared to around 120 hours for standard Zinc plating.
What is the zinc-nickel plating standard (e.g., AMS2417)?
Standards like AMS2417 (used in aerospace) and ASTM B841 specify plating thickness, composition, and performance. Always consult these specs to match customer requirements.
How does zinc-nickel perform in galvanic corrosion scenarios?
Zinc-Nickel is less prone to galvanic corrosion when paired with aluminum or steel components. It provides better electrochemical stability than regular zinc.
What’s the difference between nickel and chrome plating?
Nickel adds corrosion resistance and appearance, while chrome is harder and used for decorative or wear-resistant surfaces. Zinc-based coatings focus on protection, not aesthetics.
Need Help Choosing the Right Coating?
Still unsure which plating suits your fastener project? Contact us for expert guidance, material compatibility checks, and test reports. Whether you’re supplying infrastructure, automotive systems, or custom assemblies—we’ll help you make the right call.
Contact Hengrui Fastener for Custom fastener
For specialized applications that require custom solutions, Hengrui Fastener offers high-quality, customizable fasteners. Whether you need a specific size, material, or finish, Hengrui can provide tailored fasteners to meet your exact requirements. Contact Hengrui Fastener to learn more about our products and services.






